The success of the distance education system depends on digital access and parental attention.
Digital inequalities are preventing society from fully embracing distance learning, concludes a recent Human Development Monitoring Research report conducted by INGEV-TAM in collaboration with Istanbul Bilgi University Faculty of Communications.
The report found that lack of digital access is the most prominent factor in preventing students from being able to participate in distance learning programs. Due to socio-economic barriers, students may not have access to necessary technological devices or internet connection to be able to successfully complete their classwork.
Lack of digital literacy observed in the parents of students has emerged as another barrier in students’ access to distance education. As the constant presence of students at home places important, and at times overwhelming, responsibility on parents to take on the role of teacher in face-to-face education, the issue of digital literacy becomes more relevant.
Altogether, these report findings point to how the underlying inequalities in society have led to varying levels of digital access and literacy within different segments of the society.
We are hesitant about distance education, and we think that this type of education by itself is not enough.
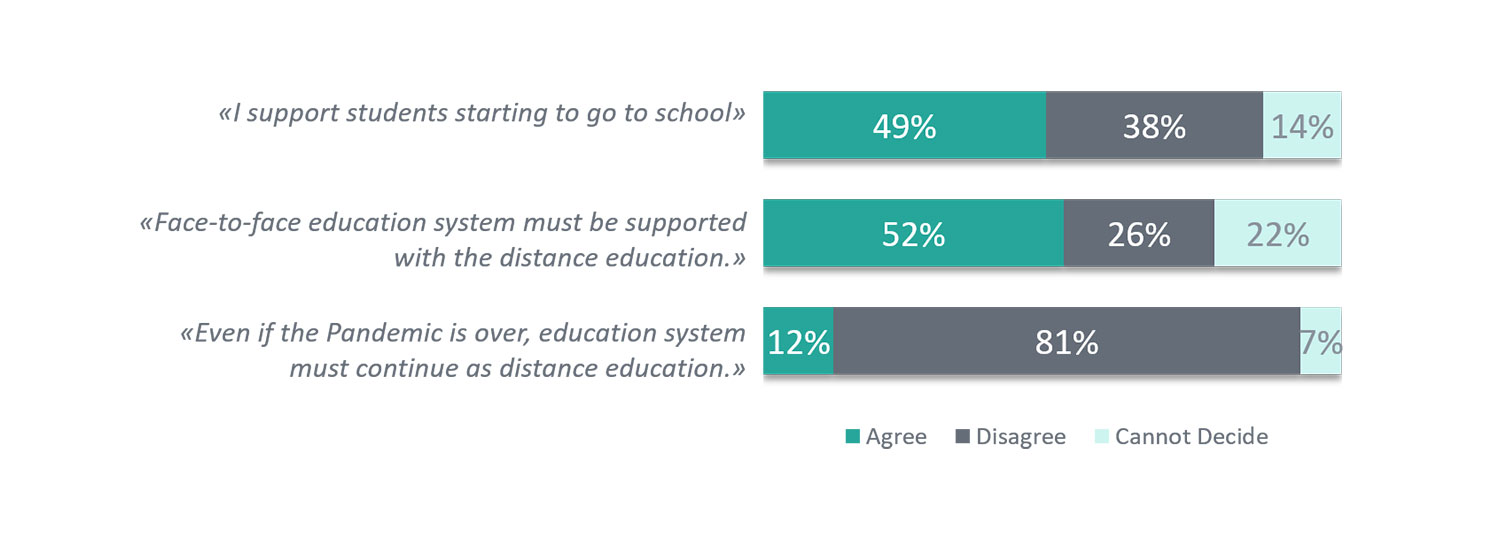
The percentage of those in Turkey who state that they trust the distance education system is 39%. Only 23% of the population thinks that this system alone is sufficient without at least partial and supplementary integration of face-to-face classes.

50% of the public supports restarting face-to-face education. Although society is reluctant to put its trust in distance education, 52% still think that after the pandemic face-to-face education should also be supplemented with distance education. On the other hand, the rate of those who think distance education should continue even after the pandemic is only 12%.
Distance education has increased inequality.
72% of the society thinks that not all students have the necessary digital access for effective distance education. This is the most critical barrier to distance education perceived by the Turkish population. 67% thinks not all parents have the knowledge to help their children access and use the distance education system. As a result, 66% of the society agrees that distance education system causes inequality among students. 63% believes that public school students are more disadvantaged compared to private school students when it comes to distance education.

This perception of inequality is manifested by the following perceptions;
- 64% states that students who receive distance education will have lower exam success;
- 53% is concerned that employers will be less likely to prefer young people who graduate from the university through distance education.
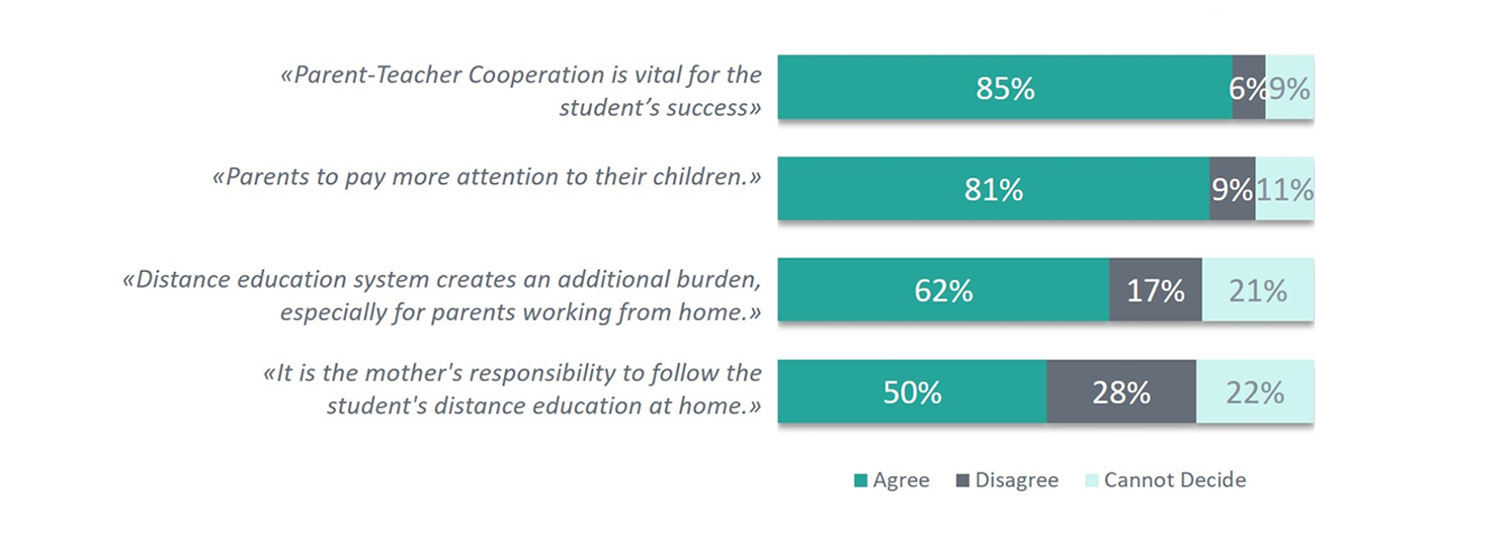
With distance education, parents have been given significant additional responsibilities.
Distance education requires parents to be significantly involved and devote more time to the education process. 85% of the society agree that the student’s success in distance education depends on parent-teacher cooperation. 81% believe that this system requires parents to pay more attention to their children. 62% think that the distance education system creates an additional burden, especially for parents working from home.
53% of the people believe that it is the mother’s responsibility to follow the student’s distance education at home.
In distance education, students cannot be motivated and socialize as much as they should.
66% of society believes that students cannot be motivated for their lessons in the distance education system. 62% states that students cannot socialize as much as they should; 63% thinks distance education is not enough for personality development. 57% believes that this system prevents the active participation of students.
It is wrong to reduce teachers’ salaries in the distance education system.
While 70% of the society finds it wrong to reduce teachers’ salaries during the distance education period, 38% think teachers are not even paid the wages they deserve during this period. On the other hand, 62% of the society states that most teachers need technical support in developing digital course content. 40% of them believes that teachers’ work intensity has increased.
The research was carried out between 8 November to 10 December 2020 according to regions identified by Turkstat Statistical Regional Unit Classifications Level 2 with a computer-assisted telephone interviewing method to ensure the Turkey representation. 1754 interviews were conducted within the scope of the study. The margin of error of the research is ± 2.3%.
Important Notice:
Please contact Can Çakır for further information – can.cakir@ingev.org
Tel: +90 216 540 50 21
